ecg lv strain | what is lvh on ecg ecg lv strain In LBBB, conduction delay means that impulses travel first via the right bundle . ULV and LV voltage cables, those being: Red Alloy, Cobalt, Lead, Soldering Metal, Tin and Zinc can all be crafted by hand or in a Packer, while all cables may be created using an Assembling Machine . The general crafting recipe for ULV and LV cables, Red Alloy in this specific picture. Crafting.
0 · what is lvh on ecg
1 · my lvhn sign in
2 · lvh with strain pattern meaning
3 · lvh signs on ecg
4 · left ventricular hypertrophy on ecg
5 · ecg voltage criteria for lvh
6 · ecg findings in lvh
7 · criteria for lvh on ecg
Browse a wide selection of new and used MDB TECHNOLOGY GREEN CLIMBER LV600 Forestry Equipment for sale near you at Machinery Trader United Kingdom
Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH): Markedly increased LV voltages: huge precordial R and S waves that overlap with the adjacent leads (SV2 + RV6 >> 35 mm). R .
R Wave Peak Time Rwpt - Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH) • LITFL • ECG .ECG Pearl. There are no universally accepted criteria for diagnosing RVH in .
ECG Criteria for Left Atrial Enlargement. LAE produces a broad, bifid P wave in .In LBBB, conduction delay means that impulses travel first via the right bundle .
U Waves - Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH) • LITFL • ECG Library DiagnosisLeft Axis Deviation - Left Ventricular Hypertrophy (LVH) • LITFL • ECG .ECG changes in left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) and right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH). The electrical vector of the left ventricle is enhanced in LVH, which results in large R-waves in left . The major conditions associated with LV volume overload are aortic or mitral valve regurgitation and dilated cardiomyopathy. Other causes of LVH include ventricular septal .
LVH with strain pattern can sometimes be seen in long standing severe aortic regurgitation, usually with associated left ventricular hypertrophy and systolic dysfunction. The .
ECG strain is associated with development of LV concentric remodeling, decline in LV systolic function, and LV myocardial scar after 10 years of follow‐up, although these .ECG strain pattern is associated with a higher cardiovascular risk, abnormal LV structure and function, incident heart failure, stroke and coronary artery disease. Acknowledgments OSO, . Repolarization abnormalities can cause ST segment depressions and T-wave inversions in the lateral leads, known as the left ventricular strain pattern. Let’s also refresh .
The ECG diagnosis of LVH is predominantly based on the QRS voltage criteria. The classical paradigm postulates that the increased left ventricular mass generates a .
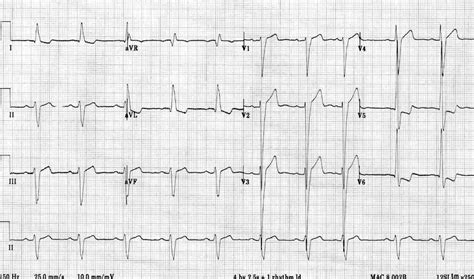
ECG strain may be an early marker of LV structural remodeling that contributes to development of adverse cardiovascular events. Clinical Trial Registration- URL: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/. . Strain is a pattern of asymmetric ST segment depression and T wave inversion. LV strain is most commonly seen in one or more leads that look at the left ventricle (leads I, aVL, . Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH): Markedly increased LV voltages: huge precordial R and S waves that overlap with the adjacent leads (SV2 + RV6 >> 35 mm). R-wave peak time > 50 ms in V5-6 with associated QRS broadening. LV strain pattern with ST depression and T-wave inversions in I, aVL and V5-6.ECG changes in left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) and right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH). The electrical vector of the left ventricle is enhanced in LVH, which results in large R-waves in left-sided leads (V5, V6, aVL and I) and deep S-waves in right-sided chest leads (V1, V2).
The major conditions associated with LV volume overload are aortic or mitral valve regurgitation and dilated cardiomyopathy. Other causes of LVH include ventricular septal defects, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and physiologic changes associated with intense athletic training. LVH with strain pattern can sometimes be seen in long standing severe aortic regurgitation, usually with associated left ventricular hypertrophy and systolic dysfunction. The sensitivity of LVH strain pattern on ECG as a measure of LVH has ranged from 3.8% to 50% in various reports [1]. ECG strain is associated with development of LV concentric remodeling, decline in LV systolic function, and LV myocardial scar after 10 years of follow‐up, although these associations were not observed in ECG LV hypertrophy.
zonnebril voor vrouwen prada
ECG strain pattern is associated with a higher cardiovascular risk, abnormal LV structure and function, incident heart failure, stroke and coronary artery disease. Acknowledgments OSO, AAA, OOO and BLS initiated the study. Repolarization abnormalities can cause ST segment depressions and T-wave inversions in the lateral leads, known as the left ventricular strain pattern. Let’s also refresh ourselves with the STEMI criteria [1] : The ECG diagnosis of LVH is predominantly based on the QRS voltage criteria. The classical paradigm postulates that the increased left ventricular mass generates a stronger electrical field, increasing the leftward and posterior QRS forces, reflected in .ECG strain may be an early marker of LV structural remodeling that contributes to development of adverse cardiovascular events. Clinical Trial Registration- URL: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/. Unique identi er: NCT00005487. (J Am Heart Assoc. 2017;6: — fi. e006624. DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.117.006624.)
Strain is a pattern of asymmetric ST segment depression and T wave inversion. LV strain is most commonly seen in one or more leads that look at the left ventricle (leads I, aVL, V4, V5, V6); less commonly it can be seen in inferior leads. Left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH): Markedly increased LV voltages: huge precordial R and S waves that overlap with the adjacent leads (SV2 + RV6 >> 35 mm). R-wave peak time > 50 ms in V5-6 with associated QRS broadening. LV strain pattern with ST depression and T-wave inversions in I, aVL and V5-6.ECG changes in left ventricular hypertrophy (LVH) and right ventricular hypertrophy (RVH). The electrical vector of the left ventricle is enhanced in LVH, which results in large R-waves in left-sided leads (V5, V6, aVL and I) and deep S-waves in right-sided chest leads (V1, V2).
The major conditions associated with LV volume overload are aortic or mitral valve regurgitation and dilated cardiomyopathy. Other causes of LVH include ventricular septal defects, hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, and physiologic changes associated with intense athletic training. LVH with strain pattern can sometimes be seen in long standing severe aortic regurgitation, usually with associated left ventricular hypertrophy and systolic dysfunction. The sensitivity of LVH strain pattern on ECG as a measure of LVH has ranged from 3.8% to 50% in various reports [1]. ECG strain is associated with development of LV concentric remodeling, decline in LV systolic function, and LV myocardial scar after 10 years of follow‐up, although these associations were not observed in ECG LV hypertrophy.
ECG strain pattern is associated with a higher cardiovascular risk, abnormal LV structure and function, incident heart failure, stroke and coronary artery disease. Acknowledgments OSO, AAA, OOO and BLS initiated the study. Repolarization abnormalities can cause ST segment depressions and T-wave inversions in the lateral leads, known as the left ventricular strain pattern. Let’s also refresh ourselves with the STEMI criteria [1] : The ECG diagnosis of LVH is predominantly based on the QRS voltage criteria. The classical paradigm postulates that the increased left ventricular mass generates a stronger electrical field, increasing the leftward and posterior QRS forces, reflected in .ECG strain may be an early marker of LV structural remodeling that contributes to development of adverse cardiovascular events. Clinical Trial Registration- URL: https://www.clinicaltrials.gov/. Unique identi er: NCT00005487. (J Am Heart Assoc. 2017;6: — fi. e006624. DOI: 10.1161/JAHA.117.006624.)
what is lvh on ecg

Незаметно пролетел еще один год, за окном переменчивая зима, и пришло время объявить очередной многими любимый конкурс «Свадьба года».
ecg lv strain|what is lvh on ecg